Cigarette Beetle
- Article
- Cigarette Beetle
Cigarette Beetle
Scientific Name: Lasioderma serricorne
How to identify a cigarette beetle
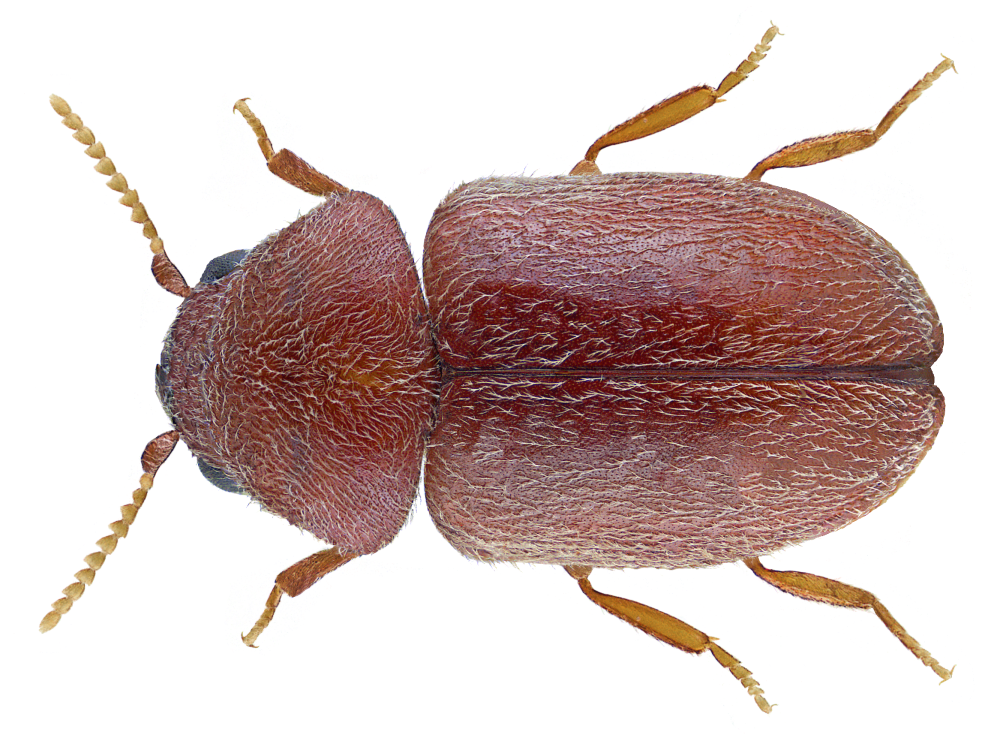
The adult beetle is light brown, small, oval and about 3 mm long. The head and prothorax are bent downward so as to give the insect a strongly humped appearance. It has occasionally been confused with the drugstore beetle (Stegobium paniceum) but L. serricorne has serrate antennae and smooth elytra, whereas in S. paniceum the last 3 antennal segments are long and broad, forming a distinct "club” and the elytra are striate. The larvae of the two species are also similar.

Where are cigarette beetles commonly found?
Apart from tobacco products, these beetles will also attack a wide range of foodstuffs including grains, seeds, herbs, spices, paprika, dog food, nuts and biscuits.
Why are cigarette beetles considered a pest?
Stored product pests are responsible for enormous losses in may ways:
-
Losses due to direct consumption
-
Spoilage and loss of commodity quality
-
Contamination
-
Encouragement of mould growth in affected material
-
Economic losses
What is the biology and lifecycle of cigarette beetles?
The female lays her oval, whitish eggs in and about the food materials and they hatch in 6 to 10 days in warm weather. There are 4 to 6 larval instars. The fully-grown larvae are about 4 mm long, curved, hairy and pupate in silken cocoons covered with bits of foodstuffs. The life cycle may require 40 to 50 days and there are usually 3 to 6 generations per year. The developmental period is affected by both humidity and temperature.
Chemicals Required to Control Cigarette Beetle
A range of traps using pheromones and other attractants are available
-
These pheromone traps are designed as monitoring devices to determine whether a species is present, where the hotspots are and whether the numbers are high enough to justify an insecticide treatment
-
Traps are designed for monitoring in commercial environments
-
Traps can be effective as control measures in domestic situations (smaller areas)
Disrupters are a relatively new technology that can be used as part of an IPM program
-
The pheromone disrupts mating, breaking the breeding cycle
-
Disrupters can significantly reduce the need for spraying in commercial accounts
Management Tips for Cigarette Beetle
Residential treatments - Thorough inspection to find the source of the infestation
-
Check all food cupboards
-
Check open and unopened packets and containers
-
Dispose of any infested materials
-
If source cannot be identified check roof void / sub-floor
-
Carry out spot treatment to storage area surfaces if required
-
Use of pheromone traps to prevent future problems / monitor activity can be considered
Commercial treatments - Thorough inspection to find the source of the infestation
-
Infested stock will need to be disposed of or treated using grain protectants or fumigation options
-
Space sprays (often pyrethrum based) and surface sprays can be considered to target adults after (larvae) infestation has been controlled
-
Use of pheromone traps to prevent future problems / monitor activity can be considered
PRODUCT SOLUTIONS
-
 Storgard Dome Ultra Combi Quick Change Broad Spectrum Beetle Trap Kit
Storgard Dome Ultra Combi Quick Change Broad Spectrum Beetle Trap KitThe Storgard Dome Ultra Combi Quick Change monitoring system is a pre-baited, high-powered, and cost-effective method of detecting beetle activity at the earliest possible stages.
-
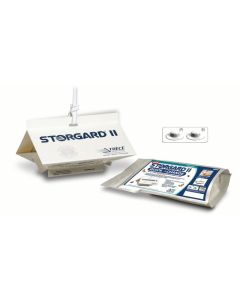 Storgard II Ultra Combi Quick Change Moth & Beetle Monitoring System
Storgard II Ultra Combi Quick Change Moth & Beetle Monitoring SystemA pack of 6 pre-baited Storgard II Ultra Combi Quick Change Moth & Beetle Monitoring traps
-
 SightTrap Kit - Remote Insect Monitoring
SightTrap Kit - Remote Insect MonitoringSightTrap is an insect monitoring device that will provide daily images, insect identification, and insect population counts allowing for the pest professional to do what they are paid to do, solve pest problems.
-
 SightTrap Glueboard & PTL Multi Species Lure
SightTrap Glueboard & PTL Multi Species LureA glueboard and PLT Pheromone Bullet Lures designed for use with the SightTrap Insect Monitoring System. The lure attracts most common stored product beetles and moths, with PTL representing the Plodia/Trogoderma/Lasioderma insects.
-
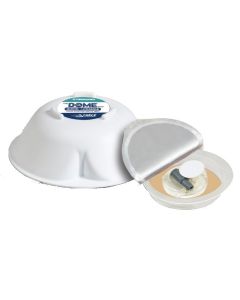 Storgard Dome Ultra Combi Refill Kit (Pack of 24)
Storgard Dome Ultra Combi Refill Kit (Pack of 24)Pack of 24 refills for the Storgard Dome Ultra Combi Quick Change monitoring system
JOIN OUR NEWSLETTER NOW!
Be the first to hear about the latest specials, products, tips and ideas.









