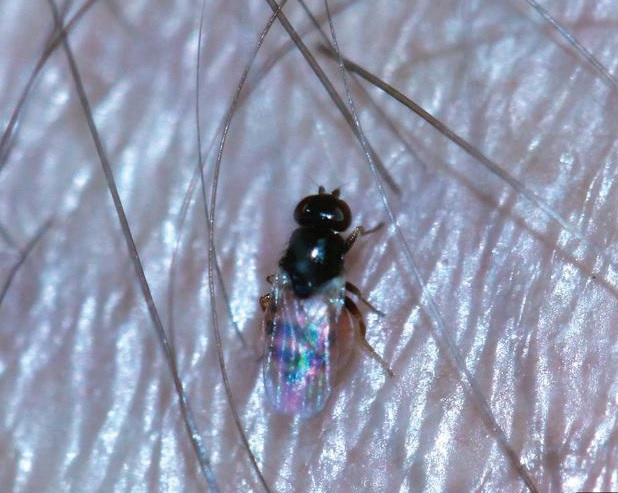
Clothes Moth
- Article
- Clothes Moth
Clothes Moth
Scientific Name: Tineola bisselliella
How to identify a clothes moth
There are actually two main species of clothes moth, the webbing clothes moth and the case-making clothes moth. The adult Webbing moth is light, gold coloured less than 1 cm long. The adult case-making moth is darker with faint dark spots. The larvae of both are cream coloured with a dark head.
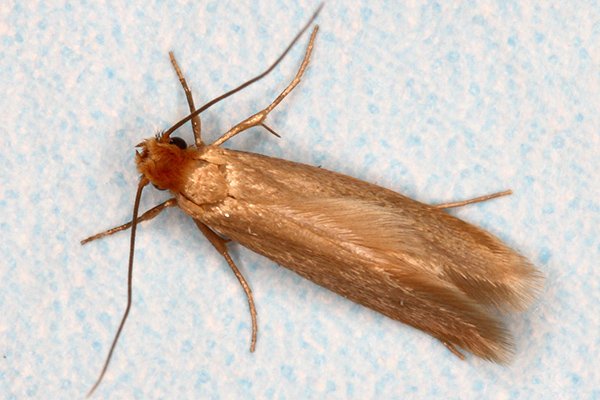

Where are clothes moths commonly found?
Generally, clothes moths are more common in the coastal areas of Australia, where the humidity helps their development. The case-making clothes moth prefers warmer parts of Australia, whereas the webbing clothes moth can be found all over Australia.
Clothes moths eat a wide range of animal fabrics, but primarily fabrics containing wool. They will also damage fur, silk, feather and leather.
Clothes moths are poor flyers, likely to be hiding in dark areas near to where the larvae are feeding.
Why are clothes moths considered a pest?
Clothes moths are considered a pest due to the damage they cause to fabrics, cloths and curtains, also furniture and edges of carpets.
What is the biology and lifecycle of Silverfish?
The lifecycle lasts for about 65-90 days, with the female adult moths living for about 30 days and potentially laying up to 300 eggs. The larvae that hatch from the eggs do the damage, as the adult moths themselves, known as 'millers', pose no threat to your knitwear or fabrics.
Management Tips for Clothes Moth
Control:
-
Items of clothing or curtains suffering damage (or items close stored close by) should be placed in a sealed black plastic bag in the sun for 1-2 hours. This will kill any larvae / eggs. The items can then be washed. Any delicate items that may be impacted by heat should be inspected individually.
-
Any cupboards which have been sites of cloth moth activity should be treated with an insecticide spray (all shelves and drawers). Items of clothing should be removed before treatment and replaced once the treatment is dry.
-
If you suspect clothes moths presence / damage in carpets, all affected areas should be sprayed with insecticide (either aerosol or ready to use pump spray), paying particular attention to damaged areas and other areas under furniture.
Prevention:
-
Regularly vacuum all carpeted rooms, especially around the perimeter and under heavy furniture.
-
Regularly move cupboards and heavy furniture in carpeted rooms. Inspect the carpet for signs of damage and insect activity.
-
At the end of each season, wash and store clothes in a sealed bag / suitcase.
PRODUCT SOLUTIONS
-
 Perigen Defence 500EC Residual Insecticide500g/L Permethrin
Perigen Defence 500EC Residual Insecticide500g/L PermethrinPerigen Defence 500 Residual Insecticide is registered for the control of cockroaches, spiders, fleas, ants and more in domestic and commercial situations.
-
 Coopex Residual Insecticide250g/kg Permethrin
Coopex Residual Insecticide250g/kg PermethrinCoopex Residual Insecticide is a wettable powder registered for the residual control of cockroaches, ants, carpet beetles, spiders, clothes moths, bed bugs, silverfish and mosquitoes.
-
 Fury 120 SC Insecticide 1L80g/L Bifenthrin, 40g/L Alpha-Cypermethrin
Fury 120 SC Insecticide 1L80g/L Bifenthrin, 40g/L Alpha-CypermethrinFury 120 SC Insecticide is specifically formulated to create a superior, longer-lasting strength general insecticide that works in two powerful ways to rid your clients of all general household pests.
-
 Chaindrite Extra Strength Crawling Insect Spray1.4g/kg Imiprothin and 2g/kg Cypermethrin
Chaindrite Extra Strength Crawling Insect Spray1.4g/kg Imiprothin and 2g/kg CypermethrinChaindrite Crawling Insect Spray is a new low odour oil-based professional aerosol insecticide with a powerful flush and kill effect on cockroaches. Chaindrite is an easy to apply aerosol “without the splutter”.This product is an excellent knockdown and flushing agent and has long term residual activity.
-
 Starrdust PRO Insecticidal Dust 10kg20g/kg Permethrin 40:60, 5g/kg Triflumuron
Starrdust PRO Insecticidal Dust 10kg20g/kg Permethrin 40:60, 5g/kg TriflumuronStarrdust PRO Insecticidal Dust is a ready-to-use, broad spectrum insecticide with a unique formulation. It controls a wide range of insect pests including cockroaches, silverfish, spiders, ants, fleas, carpet beetles, bed bugs, European wasps, feral honey bees, bird mites, subterranean termites, hide beetles, and 3 new pests not on any dust product in Australia – millipedes, woodlice and clothes moths.
-
 Maxum PRO 125 SC Insecticide 500mL125g/L Beta Cyfluthrin
Maxum PRO 125 SC Insecticide 500mL125g/L Beta CyfluthrinMaxumPRO is a robust, fast-acting, knock-down, broad spectrum insecticide for general insect control in domestic and commercial situations, as well as for the control of pest insects of turf and ornamental plants.
-
 Starrdust Pro Duckbill + ‘One-Shot’ 400g20g/kg Permethrin 40:60, 5g/kg Triflumuron
Starrdust Pro Duckbill + ‘One-Shot’ 400g20g/kg Permethrin 40:60, 5g/kg TriflumuronThe StarrdustPRO ‘ONE-SHOT’ is a ready-to-use pod that screws straight onto the StarrdustPRO DUCKBILL Duster head. It is prefilled with 400 grams of premium StarrdustPRO Industrial Strength dusting powder.
-
 Battleaxe Pro Aerosol 420g20g/kg propoxur, 2g/kg tetramethrin, 10g/kg piperonyl butoxide
Battleaxe Pro Aerosol 420g20g/kg propoxur, 2g/kg tetramethrin, 10g/kg piperonyl butoxideBattleaxe PRO Professional Crack & Crevice is an aerosol formulation containing both long lasting and vapour-acting knockdown components.
-
 PY Mist Insecticide4g/L Pyrethrins, 12g/L Piperonyl Butoxide
PY Mist Insecticide4g/L Pyrethrins, 12g/L Piperonyl ButoxidePY Mist is a ready to use insecticide for the control of a range of insect pests and is applied using a cold fogger / portable fogging machine.
-
 Delta Pro 25SC Professional Insecticide25g/L Deltamethrin
Delta Pro 25SC Professional Insecticide25g/L DeltamethrinFor the control of a range of insect pests such as spiders, cockroaches, flies, ants, mosquitoes in various situations.
-
 PY Spray Aerosol Insecticide10 g/kg pyrethrin and 50 g/kg piperonyl butoxide
PY Spray Aerosol Insecticide10 g/kg pyrethrin and 50 g/kg piperonyl butoxidePY Spray Aerosol Insecticide is a ready to use professional aerosol for control of a range of insect pests in various situations. Suitable for crack and crevice applications. PY Spray Aerosol Insecticide is an industrial strength spray, suitable for flushing or as a space spray.
-
 PY Fog Insecticide4g/L Pyrethrins, 12g/L Piperonyl Butoxide
PY Fog Insecticide4g/L Pyrethrins, 12g/L Piperonyl ButoxidePY Fog is a ready to use, broad spectrum insecticide for the control of a range of insect pests in various situations using a thermal fogging machine.
-
 Cislin 25 Professional Insecticide25g/L Deltamethrin
Cislin 25 Professional Insecticide25g/L DeltamethrinCislin 25 Professional Insecticide is a broad spectrum low odour insecticide with excellent residual activity.
-
 Delforce Residual Insecticide 10SC10g/L Deltamethrin
Delforce Residual Insecticide 10SC10g/L DeltamethrinDelforce Residual Insecticide 10SC is a water-based insecticide for the quick knockdown of spiders and general insects at very low doses. Delforce is also formulated for the control cockroaches, fleas, spiders, ants, silverfish and of a range other insects.
-
 Suspend Flexx Insecticide25g/L Deltamethrin
Suspend Flexx Insecticide25g/L DeltamethrinSuspend Flexx Insecticide is a synthetic pyrethroid (3A) formulation for the knockdown and residual control of a range of insect pests in various indoor and outdoor situations.
-
 Suspend Flexx Insecticide 500mL25g/L Deltamethrin
Suspend Flexx Insecticide 500mL25g/L DeltamethrinSuspend Flexx Insecticide is a synthetic pyrethroid (3A) formulation for the knockdown and residual control of a range of insect pests in various indoor and outdoor situations.
-
 Suspend Flexx Insecticide 3L25g/L Deltamethrin
Suspend Flexx Insecticide 3L25g/L DeltamethrinSuspend Flexx Insecticide is a synthetic pyrethroid (3A) formulation for the knockdown and residual control of a range of insect pests in various indoor and outdoor situations.
-
 SX Fly Inn Pheromone Replacement Pads for Clothes Moth (Pack of 10)
SX Fly Inn Pheromone Replacement Pads for Clothes Moth (Pack of 10)Replacement pheromone glue pads for the SX Fly Inn Fruit Fly Lure, targeting Clothes Moth (Tineola bisselliella).
-
 Starrdust PRO One-Shot Insecticidal Dust 400g20g/kg Permethrin, 5g/kg Triflumuron
Starrdust PRO One-Shot Insecticidal Dust 400g20g/kg Permethrin, 5g/kg TriflumuronThe Starrdust PRO One-Shot Insecticidal Dust 400g is an industrial-strength dust designed for use with the Starrdust PRO Duckbill Duster. It is a ready-to-use broad-spectrum insecticide with a unique formulation. It controls a wide range of insect pests including cockroaches, silverfish, spiders, ants, fleas, carpet beetles, bed bugs, European wasps, feral honey bees, bird mites, subterranean termites, hide beetles, millipedes, woodlice and clothes moths.
-
 Starrdust PRO One-Shot Insecticidal Dust 19 x 400g + Duckbill20g/kg Permethrin, 5g/kg Triflumuron
Starrdust PRO One-Shot Insecticidal Dust 19 x 400g + Duckbill20g/kg Permethrin, 5g/kg TriflumuronA convenient kit of 19 x Starrdust PRO One-Shot Insecticidal Dust 400g Pods and a bonus Duckbill Duster. StarrDust PRO is an industrial-strength dust designed for use with the Starrdust PRO Duckbill Duster. It is a ready-to-use broad-spectrum insecticide with a unique formulation. It controls a wide range of insect pests including cockroaches, silverfish, spiders, ants, fleas, carpet beetles, bed bugs, European wasps, feral honey bees, bird mites, subterranean termites, hide beetles, millipedes, woodlice and clothes moths.
-
 Delta Pro 25SC Professional Insecticide - 1L25g/L Deltamethrin
Delta Pro 25SC Professional Insecticide - 1L25g/L DeltamethrinFor the control of a range of insect pests such as spiders, cockroaches, flies, ants, mosquitoes in various situations.
-
 Delta Pro 25SC Professional Insecticide-5L25g/L Deltamethrin
Delta Pro 25SC Professional Insecticide-5L25g/L DeltamethrinFor the control of a range of insect pests such as spiders, cockroaches, flies, ants, mosquitoes in various situations.
-
 Tempo Residual Insecticide 1L25 g/L betacyfluthrin
Tempo Residual Insecticide 1L25 g/L betacyfluthrinTempo Residual Insecticide is a fast-acting, knock-down, broad-spectrum insecticide for general insect control in domestic and commercial situations, as well as for the control of pest insects of turf and ornamental plants.
-
 Starrdust PRO Insecticidal Dust20g/kg Permethrin 40:60, 5g/kg Triflumuron
Starrdust PRO Insecticidal Dust20g/kg Permethrin 40:60, 5g/kg TriflumuronStarrdust PRO Insecticidal Dust is a ready-to-use, broad spectrum insecticide with a unique formulation. It controls a wide range of insect pests including cockroaches, silverfish, spiders, ants, fleas, carpet beetles, bed bugs, European wasps, feral honey bees, bird mites, subterranean termites, hide beetles, and 3 new pests not on any dust product in Australia – millipedes, woodlice and clothes moths.
-
 Starrdust PRO Insecticidal Dust 2kg20g/kg Permethrin 40:60, 5g/kg Triflumuron
Starrdust PRO Insecticidal Dust 2kg20g/kg Permethrin 40:60, 5g/kg TriflumuronStarrdust PRO Insecticidal Dust is a ready-to-use, broad spectrum insecticide with a unique formulation. It controls a wide range of insect pests including cockroaches, silverfish, spiders, ants, fleas, carpet beetles, bed bugs, European wasps, feral honey bees, bird mites, subterranean termites, hide beetles, and 3 new pests not on any dust product in Australia – millipedes, woodlice and clothes moths.
-
 Killgerm AF Demi-Diamond Tineola Bisselliella Pheromone Monitoring Glue Pads (Pack of 10)Replacement Clothes Moth Glue Pads
Killgerm AF Demi-Diamond Tineola Bisselliella Pheromone Monitoring Glue Pads (Pack of 10)Replacement Clothes Moth Glue PadsKillgerm AF Demi-Diamond Clothes Moth (Tineola Bisselliella) Glue Pads is an adhesive board that targets clothes moths with a pheromone attractant using slow-release matrix technology.
JOIN OUR NEWSLETTER NOW!
Be the first to hear about the latest specials, products, tips and ideas.









