Starlings
- Article
- Starlings
Starlings
SCIENTIFIC NAME: Sturnus vulgaris
HOW TO IDENTIFY A STARLING
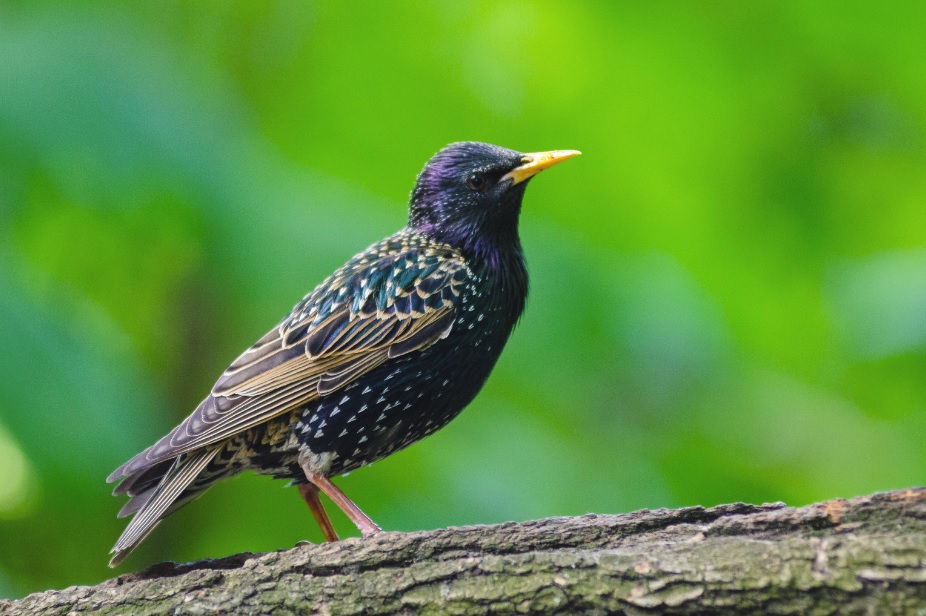
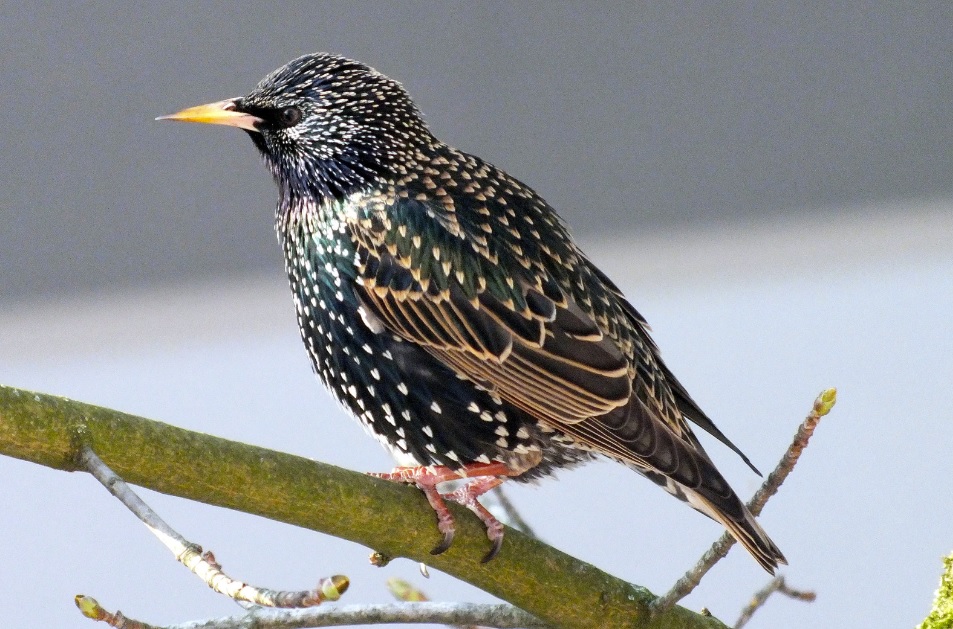
The Common Starling has a wide variation in plumage. Both sexes are similar, although the female is less glossy than the male. In autumn, when the plumage is new, birds are glossed black, with a purple and green shine, and the tips of the body feathers have large white spots. At this time the bill is dark and the legs are brown. With wear, the white spots are lost, while the bill and legs turn yellow. During the breeding season adults become glossy-black without any spots. Young birds are dull grey-brown.

WHERE ARE STARLINGS COMMONLY FOUND?
The Common Starling is a prominent bird in open cultivated areas, and is a well-known pest of orchards. However, Starlings can be found around human habitation nesting in roof voids, ledges/awnings, under sarking or in holes in walls.
WHY ARE STARLINGS CONSIDERED A PEST?
Starlings a considered a pest because of the damage to buildings and guttering due to acidic nature of droppings. Noise pollution is also a problem when Starlings are present in large numbers.
Starlings are also a carriers of bird mites.

WHAT IS THE BIOLOGY AND LIFECYCLE OF A STARLING?
Breeding season from Sept to January with two clutches of 5-7 eggs each.
The life span of a Starling is 2-3 years.
Management Tips for Starlings
To effectively protect a building from a bird problem, it often requires a combination of products. Take into account the following in designing your bird protection system:
-
Bird species/pressure
-
Building structure
-
Location of problem
-
Installation issues
-
Durability requirements
-
Aesthetic requirements
-
Safety/environmental concerns
-
Cost
A wide range of bird protection systems are available to effectively protect a building from a bird problem with various different methods:
Area exclusions - When installed correctly, bird netting provides the most complete, humane and durable system for bird exclusion.
Ledge exclusion - Large Birds: A system of spikes, wires and spiders can be utilised to discourage birds from landing on ledges. All Birds: a system of slopes and shock systems can be utilised.
Scare devices - A variety of scarer and repeller devices are available
Traps - For humane and safe removal of birds, particularly in sensitive areas
Avicide - For pigeons, sparrows and starlings. Only for application by authorised persons.
Solar panel protection - Solar panel exclusion kits are designed to prevent nesting under solar arrays - avoids expensive damage and reduction in efficiency due to bird droppings on panels.
Disease protection - PX Ornikill can be used as a clean up product and disease protection treatment, kill a range of disease organisms associated with pest birds such as ornithosis and psittacosis.
PRODUCT SOLUTIONS
-
 VEXO GX21 Stainless Steel 2 Bird Spikes (Gutter) - 10m BundlePack of 10 x 1m Spikes
VEXO GX21 Stainless Steel 2 Bird Spikes (Gutter) - 10m BundlePack of 10 x 1m SpikesVEXO GX21 gutter spikes are stainless steel bid spikes uniquely designed and shaped to prevent birds from perching and nesting in gutters.
-
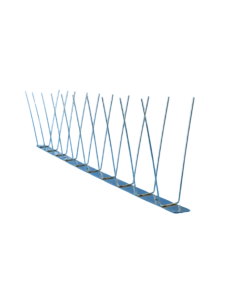 VEXO SS21 Stainless Steel 2 Bird Spike (Narrow) - 10m BundlePack of 10 x 1m Spikes
VEXO SS21 Stainless Steel 2 Bird Spike (Narrow) - 10m BundlePack of 10 x 1m SpikesVEXO SS21 Narrow Bird Spikes are lightweight fully stainless steel spikes that provide discrete protection against pigeons, mynas, starling, galahs, magpies and cockatoos.
-
 VEXO SS41 Stainless Steel 4 Bird Spike (Wide) - 10m BundlePack of 10 x 1m Spikes
VEXO SS41 Stainless Steel 4 Bird Spike (Wide) - 10m BundlePack of 10 x 1m SpikesVEXO SS41 Wide Bird Spikes are stainless steel spikes that provide discrete protection against pigeons, mynas, starling, galahs, magpies and cockatoos. SS41 spikes are the most popular bird spike as a durable versatile solution against pest birds.
-
 VEXO SS61 Stainless Steel 6 Bird Spikes (Ultra Wide) - 10m BundlePack of 10 x 1m Spikes
VEXO SS61 Stainless Steel 6 Bird Spikes (Ultra Wide) - 10m BundlePack of 10 x 1m SpikesVEXO SS61 Ultra Wide Bird Spikes are stainless steel spikes that provide discrete protection against pigeons, mynas, starling, galahs, magpies and cockatoos. SS61 spikes provide extra wide protection coverage against medium size birds.
-
 VEXO SW71 Stainless Steel 4 Bird Spikes (Solar / Eave) - 10m BundlePack of 10 x 1m Spikes
VEXO SW71 Stainless Steel 4 Bird Spikes (Solar / Eave) - 10m BundlePack of 10 x 1m SpikesVEXO SW71 Eave and Solar Bird Spikes are stainless steel spikes that provide discrete protection against pigeons, mynas, starling, galahs, magpies, and cockatoos. SW71 spikes are highly versatile, used to protect eaves, solar panels, and window ledges.
-
 Vexo MZ30 Solarguard Pro Mesh KitReady to install
Vexo MZ30 Solarguard Pro Mesh KitReady to installVEXO Solarguard Pro Mesh Kits are designed to protect solar panel installations, the roof and electrical wiring from damage caused by rodents, birds and possums by preventing access. Use this solar panel mesh to build an effective physical barrier around your solar panels to keep birds and rodents from nesting underneath.
-
 Premium Bird Net 19mm
Premium Bird Net 19mmGlobe's 19mm Premium Bird Netting offers reliable and effective bird-proofing solutions for properties facing challenges from both smaller birds and larger species like pigeons and seagulls. Crafted from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), this premium bird netting is designed to endure harsh weather conditions, making it ideal for both urban and rural settings with any level of bird infestation.
-
 PCO Bird 3 Spike 15m
PCO Bird 3 Spike 15mProfessional, Stainless Steel, Bird Deterrent Spikes. There is 15m of bird spikes per box (30 x 50cm strips), with a 12.5cm top width span.
-
 Bird Free Optical Gel Deterrent with Magnet - 15 PackReady to install
Bird Free Optical Gel Deterrent with Magnet - 15 PackReady to installBird Free Optical Gel with Magnetic Base is a revolutionary bird repellent solution consisting of small, pre-loaded dishes with a magnetic base, filled with a firm, weather-resistant gel making it easy to install. Utilising a unique multi-sensory approach to deter birds, Bird Free Optical Gel creates an environment that birds perceive as uncomfortable and unsafe, prompting them to abandon the area.
-
 Bird Free Optical Gel Deterrent - 15 PackReady to install
Bird Free Optical Gel Deterrent - 15 PackReady to installBird Free Optical Gel is a revolutionary bird repellent solution that consists of small, pre-loaded dishes filled with a firm, weather-resistant gel that is discreet and easy to install. Utilising a unique multi-sensory approach to deter birds, Bird Free Optical Gel creates an environment that birds perceive as uncomfortable and unsafe, prompting them to abandon the area entirely. Approved by the APVMA for use in Australia, it provides a humane, eco-friendly, and long-lasting alternative to conventional bird control methods.
-
 D-Ter Animal & Bird RepellentSafe & Effective
D-Ter Animal & Bird RepellentSafe & EffectiveD-Ter Animal & Bird Repellent is a safe and effective repellent used to deter unwanted animals and birds. D-Ter is ideal for use as a repellent for dogs, cats, birds, possums, kangaroos, bandicoots and many other animals.
-
 Galvanised Wire Rope 2mm (200m Spool)
Galvanised Wire Rope 2mm (200m Spool)The Galvanised Bird Wire Rope 2mm (200m Spool) is a versatile and durable solution designed for a wide range of pest control and structural applications. Crafted from high-quality galvanised steel, this wire rope combines strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor use.
-
 Stainless Steel Wire Rope 2mm (200m Spool)
Stainless Steel Wire Rope 2mm (200m Spool)The Stainless Steel Wire Rope 2mm (200m Spool) is a professional-grade solution designed for pest control tasks and bird-proofing projects. With its robust construction and versatile applications, this wire rope is can be used for securing rodent stations to installing bird netting.
-
 VEXO K6XL Extra Large Ultra Dense Bird Spikes - 5m BundlePack of 10 x 0.5m Spikes
VEXO K6XL Extra Large Ultra Dense Bird Spikes - 5m BundlePack of 10 x 0.5m SpikesVexo K6XL Extra Large Ultra Dense Bird Spikes feature extra-long spikes providing 25% greater height and width coverage than the standard K6 model. This gives you the best of both worlds by maintaining the higher spike density required to exclude smaller pest birds while adding the extra height required to tackle taller pest species.
-
 VEXO K6 Stainless Steel Small Bird Spikes (Ultra Dense) - 5m BundlePack of 10 x 0.5m spikes
VEXO K6 Stainless Steel Small Bird Spikes (Ultra Dense) - 5m BundlePack of 10 x 0.5m spikesVEXO K6 Ultra Dense Small Bird Spikes are extra dense, light weight spikes that are designed to deter smaller birds like starlings, mynas, and sparrows. Manufactured using premium grade 304 stainless steel, this durable and versatile solution will serve as a long-lasting and reliable pest bird deterrent.
-
 VEXO GX33 Stainless Steel Bird Spikes (Ultra Dense Gutter) - 5m BundlePack of 10 x 0.5m Spikes
VEXO GX33 Stainless Steel Bird Spikes (Ultra Dense Gutter) - 5m BundlePack of 10 x 0.5m SpikesVEXO GX33 ultra dense gutter spikes are stainless steel bird spikes uniquely designed to prevent smaller birds from perching and nesting in gutters.
JOIN OUR NEWSLETTER NOW!
Be the first to hear about the latest specials, products, tips and ideas.









