Drugstore Beetle
Drugstore Beetle
Scientific Name: Stegobium paniceum
How to identify a drugstore beetle
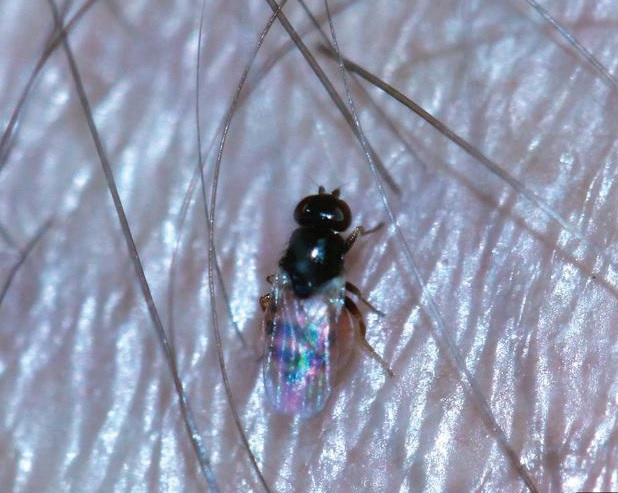
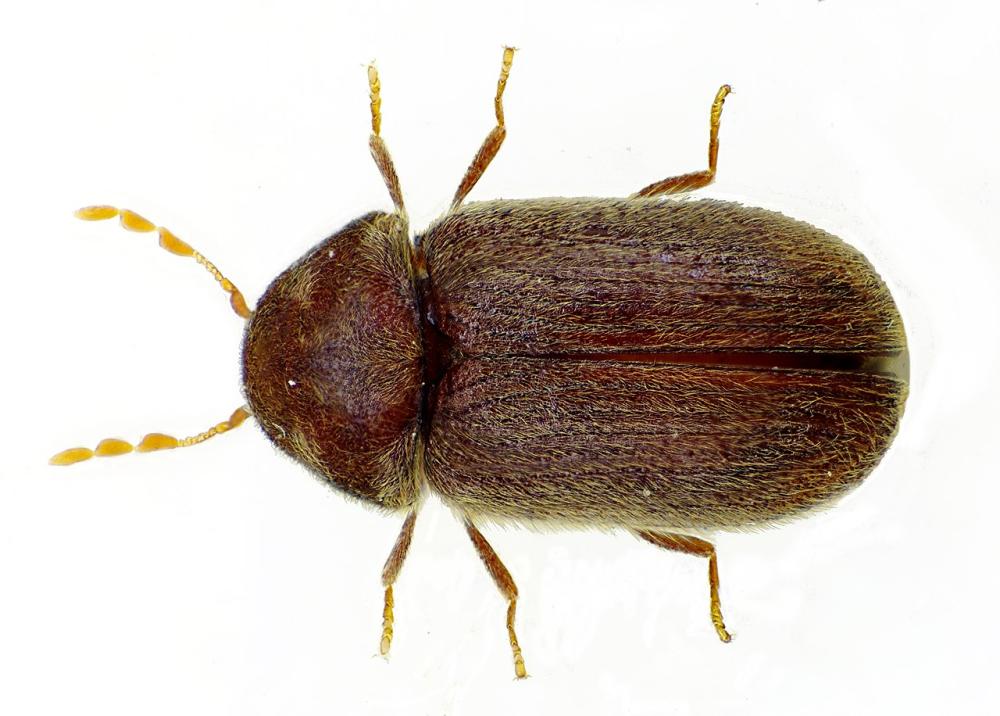
The adult is oval and globular in shape and 3.0 to 4.0 mm long. The colour is uniformly reddish to reddish brown. Very fine hairs are arranged in longitudinal rows on the elytra. The drugstore beetle can be distinguished from the cigarette beetle by the distinctly striate elytra, the 3 enlarged segments at the tips of the antennae and by the less hairy larva. The antennae are waved rapidly when the beetles are walking. If disturbed, they may “play dead” by curling up and remaining motionless.

Where are drugstore beetles commonly found?
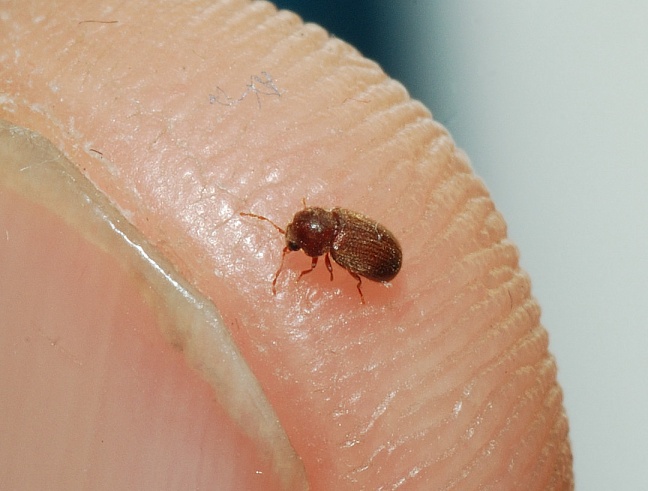
This cosmopolitan species resembles the cigarette beetle and rivals it as a pantry pest. It feeds on any of the household foods and spices, as well as wool, hair, leather, horn, museum specimens and drugs. It has been known to perforate books and wooden objects and even tin or aluminium foil and lead. This fact is not surprising considering that both this species and the Cigarette Beetle belong to the same Family (Anobiidae) as the Anobium beetle (Furniture Borer).

Why are drugstore beetles considered a pest?
Stored product pests are responsible for enormous losses in may ways:
-
Losses due to direct consumption
-
Spoilage and loss of commodity quality
-
Contamination
-
Encouragement of mould growth in affected material
-
Economic losses
What is the biology and lifecycle of drugstore beetles?
The life cycle resembles that of the cigarette beetle. The female lays her eggs singly in cracks and crevices of the substrate. She may deposit around 100 eggs of her life span of about one month. As they are a Secondary Pest, the hatched larvae cannot feed upon whole grain but will search diligently for an entry point into packaged items. After feeding for at least 40 days, the larvae construct a pupal case inside the foodstuff. After metamorphosing into adults, they stay inside the pupal case for a few days before biting their way out. The adults rarely feed and are short lived.
Chemicals Required to Control Drugstore Beetle
A range of traps using pheromones and other attractants are available
-
These pheromone traps are designed as monitoring devices to determine whether a species is present, where the hotspots are and whether the numbers are high enough to justify an insecticide treatment
-
Traps are designed for monitoring in commercial environments
-
Traps can be effective as control measures in domestic situations (smaller areas)
Disrupters are a relatively new technology that can be used as part of an IPM program
-
The pheromone disrupts mating, breaking the breeding cycle
-
Disrupters can significantly reduce the need for spraying in commercial accounts
Management Tips for Drugstore Beetle
Residential treatments - Thorough inspection to find the source of the infestation
-
Check all food cupboards
-
Check open and unopened packets and containers
-
Dispose of any infested materials
-
If source cannot be identified check roof void / sub-floor
-
Carry out spot treatment to storage area surfaces if required
-
Use of pheromone traps to prevent future problems / monitor activity can be considered
Commercial treatments - Thorough inspection to find the source of the infestation
-
Infested stock will need to be disposed of or treated using grain protectants or fumigation options
-
Space sprays (often pyrethrum based) and surface sprays can be considered to target adults after (larvae) infestation has been controlled
-
Use of pheromone traps to prevent future problems / monitor activity can be considered